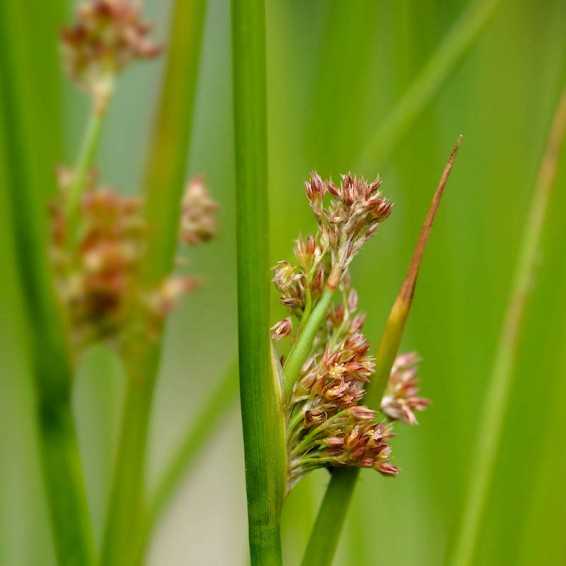
Path Rush Seeds
Juncus tenuis
- HOW TO GROW
- FAST FACTS
HOW TO GROW
Sowing: Direct sow either in late fall or early spring. Press the Juncus tenuis seed into the surface of the soil, compacting the soil very firmly. Keep the soil lightly moist until germination.
Growing: Water seedlings regularly until they become established. This plant prefers soil that is constantly moist, though it tolerates some drought. It also adapts well to various soil types such as sand, clay, and gravel. It has excellent resistance to foot traffic and highly compacted soil. It will eventually spread by rhizomes and self-seeding, even becoming weedy in good growing conditions. In addition to being a low maintenance ground cover, this plant makes an very good choice for erosion control, strengthening stream banks, or wetland restoration; it also provides forage and cover for birds and other wildlife.
Seed Saving: At the end of the season, the seed heads will begin to ripen and turn from yellow to brown. Cut the mature path rush seed heads from the stem and spread them out to dry. As they dry, the pods will open and release the tiny, dust-like seed. Separate the seed from the plant material. Store the seed in a cool, dry place.
FAST FACTS
Common Names: Poverty Rush
Latin Name: Juncus tenuis
Species Origin: US Native Grass or Sedge
Type: Native Grasses, Cool Season
Life Cycle: Perennial
USDA Zones: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
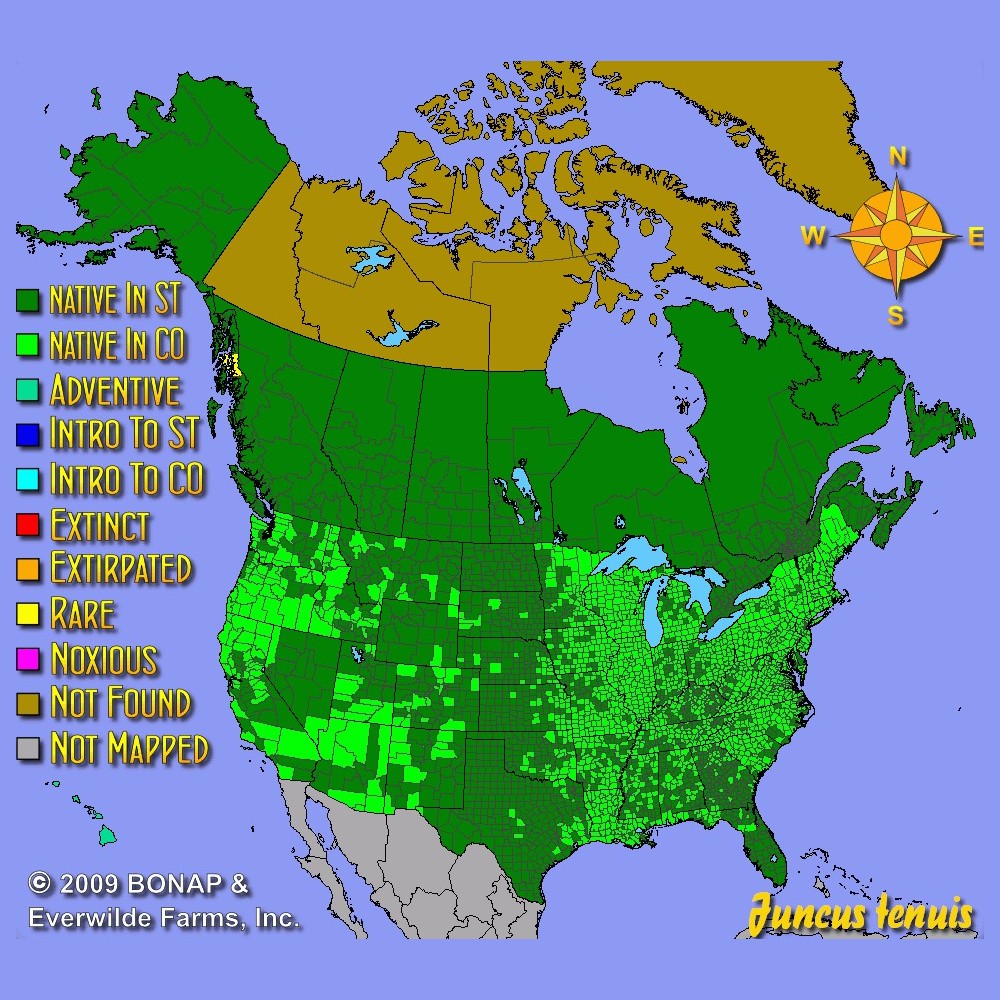
US Regions: California, Mountain, Arid/Desert, Plains/Texas, Midwest, Northern, Northeast, Southeast
Seeds per Ounce: 1,000,000
Stratification: Cold/Wet for 8 Weeks
Germination Ease: Stratify 8 Weeks
Sunlight: Full Sun, Part Sun
Height: 9 Inches
Color: Green, Brown
Bloom Season: Blooms Late Summer, Blooms Early Fall
DESCRIPTION
HOW TO GROW
Sowing: Direct sow either in late fall or early spring. Press the Juncus tenuis seed into the surface of the soil, compacting the soil very firmly. Keep the soil lightly moist until germination.
Growing: Water seedlings regularly until they become established. This plant prefers soil that is constantly moist, though it tolerates some drought. It also adapts well to various soil types such as sand, clay, and gravel. It has excellent resistance to foot traffic and highly compacted soil. It will eventually spread by rhizomes and self-seeding, even becoming weedy in good growing conditions. In addition to being a low maintenance ground cover, this plant makes an very good choice for erosion control, strengthening stream banks, or wetland restoration; it also provides forage and cover for birds and other wildlife.
Seed Saving: At the end of the season, the seed heads will begin to ripen and turn from yellow to brown. Cut the mature path rush seed heads from the stem and spread them out to dry. As they dry, the pods will open and release the tiny, dust-like seed. Separate the seed from the plant material. Store the seed in a cool, dry place.
FAST FACTS
Common Names: Poverty Rush
Latin Name: Juncus tenuis
Species Origin: US Native Grass or Sedge
Type: Native Grasses, Cool Season
Life Cycle: Perennial
USDA Zones: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
US Regions: California, Mountain, Arid/Desert, Plains/Texas, Midwest, Northern, Northeast, Southeast
Seeds per Ounce: 1,000,000
Stratification: Cold/Wet for 8 Weeks
Germination Ease: Stratify 8 Weeks
Sunlight: Full Sun, Part Sun
Height: 9 Inches
Color: Green, Brown
Bloom Season: Blooms Late Summer, Blooms Early Fall




