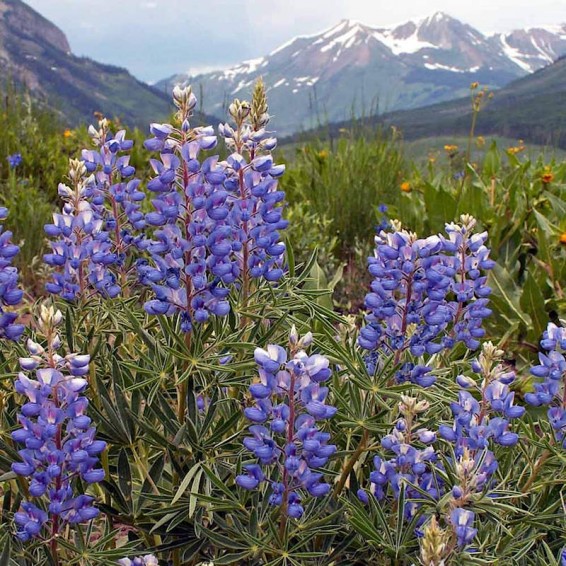
Mountain Lupine Seeds
Lupinus alpestris
- HOW TO GROW
- FAST FACTS
HOW TO GROW
Sowing: To soften the hard coating on these Lupinus Alpestris seeds, rub them lightly with sandpaper or soak them in 180 degrees F water overnight before sowing. Sow them in early spring, planting 1/2" deep. Keep the soil lightly moist until germination.
Growing: These seedlings grow very slowly and are rather fragile. Water them occasionally and protect from freezing temperatures. Mature plants thrive even in drought conditions and are known for being very fire resistant. This plant can be poisonous to livestock if present in excessive amounts. These plants resent having their roots disturbed.
Harvesting: For cut flowers, choose stems with flowers that have just opened. Strip the foliage that will fall below the water level, and place in water immediately.
Seed Saving: As the seed pods develop, watch them carefully. As soon as they ripen fully they will split and drop their seed. When the pods begin to turn brown, remove them and spread them out to dry. Remove the Lupinus Alpestris seed from the pods and store it in a cool, dry place. Keep in mind that these Mountain Lupine seeds are highly poisonous.
FAST FACTS
Common Names: Great Basin Lupine
Latin Name: Lupinus alpestris
Species Origin: US Native Wildflower
Type: Native Wildflowers
Life Cycle: Perennial
USDA Zones: 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
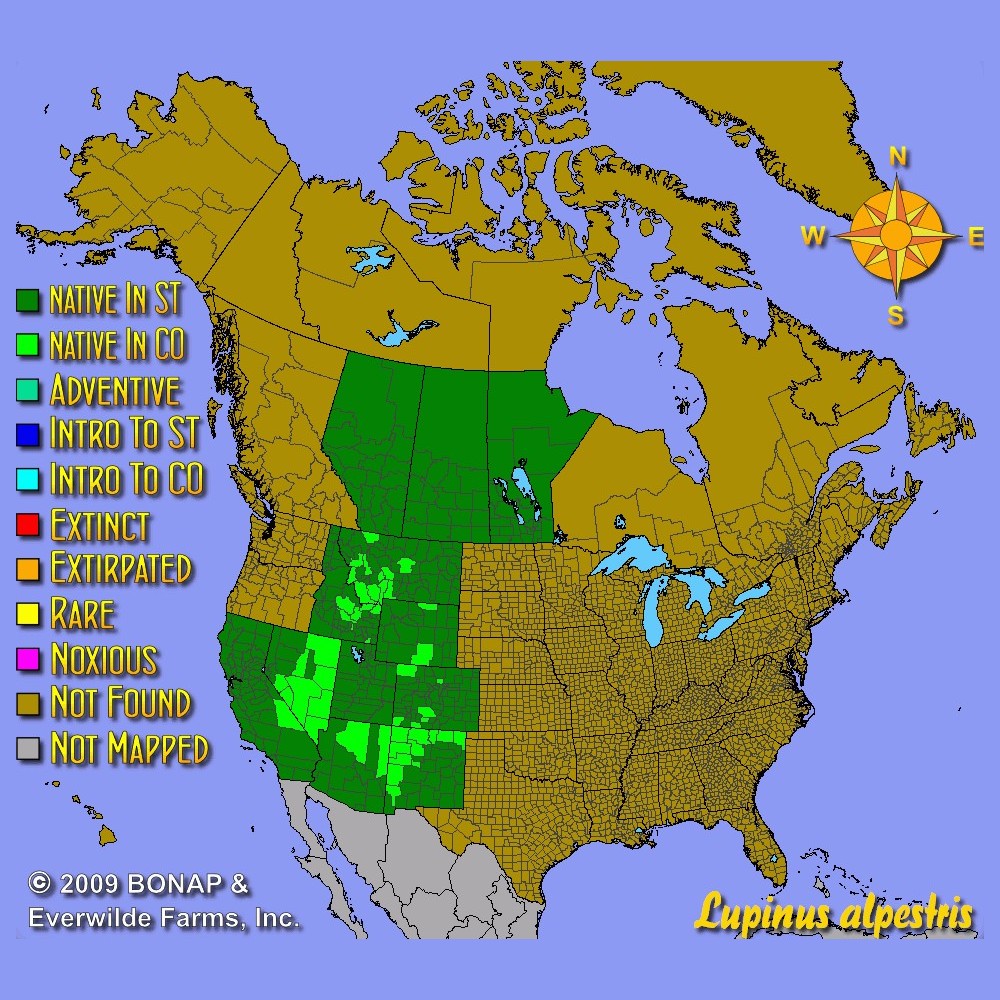
US Regions: Mountain, Arid/Desert
Seeds per Ounce: 1,100
Stratification: No Stratification
Germination Ease: No Stratification
Sunlight: Full Sun, Part Sun
Height: 20 Inches
Color: Blue
Bloom Season: Blooms Early Summer, Blooms Late Summer
Uses: Deer Resistant
DESCRIPTION
HOW TO GROW
Sowing: To soften the hard coating on these Lupinus Alpestris seeds, rub them lightly with sandpaper or soak them in 180 degrees F water overnight before sowing. Sow them in early spring, planting 1/2" deep. Keep the soil lightly moist until germination.
Growing: These seedlings grow very slowly and are rather fragile. Water them occasionally and protect from freezing temperatures. Mature plants thrive even in drought conditions and are known for being very fire resistant. This plant can be poisonous to livestock if present in excessive amounts. These plants resent having their roots disturbed.
Harvesting: For cut flowers, choose stems with flowers that have just opened. Strip the foliage that will fall below the water level, and place in water immediately.
Seed Saving: As the seed pods develop, watch them carefully. As soon as they ripen fully they will split and drop their seed. When the pods begin to turn brown, remove them and spread them out to dry. Remove the Lupinus Alpestris seed from the pods and store it in a cool, dry place. Keep in mind that these Mountain Lupine seeds are highly poisonous.
FAST FACTS
Common Names: Great Basin Lupine
Latin Name: Lupinus alpestris
Species Origin: US Native Wildflower
Type: Native Wildflowers
Life Cycle: Perennial
USDA Zones: 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
US Regions: Mountain, Arid/Desert
Seeds per Ounce: 1,100
Stratification: No Stratification
Germination Ease: No Stratification
Sunlight: Full Sun, Part Sun
Height: 20 Inches
Color: Blue
Bloom Season: Blooms Early Summer, Blooms Late Summer
Uses: Deer Resistant






